
Deploy Enterprise AI Project Assistants for Your Team.
Enterprise AI Project Assistants unlock unprecedented productivity by automating the routine tasks that slow teams down. They combine seven essential capabilities—Transcribe, Inbox, Schedule, Ops, Outreach, CRM and Iterate—to create an end-to-end workflow that turns conversations into action, orchestrates calendars, automates operations, engages clients, keeps data accurate and continuously improves.
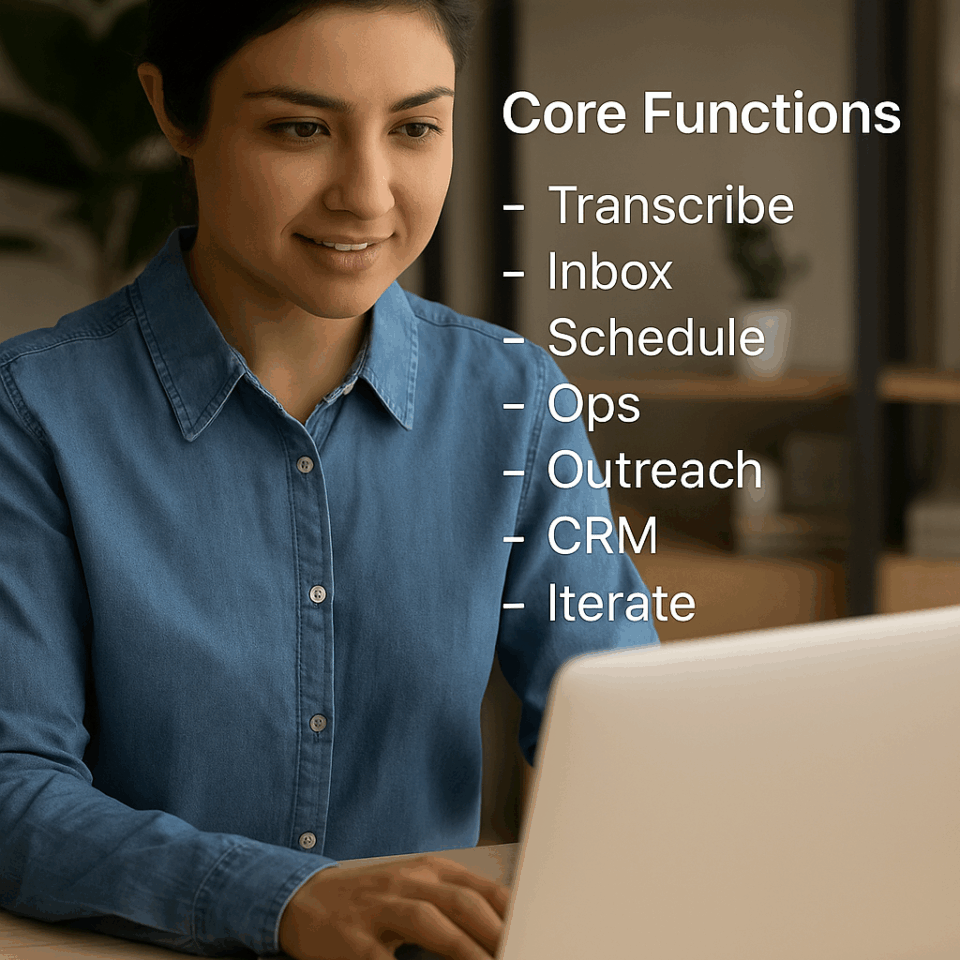
Core Functions
Enterprise AI Project Assistants are built from seven core capabilities. Each capability solves a different piece of the administrative puzzle and, when combined, they create a seamless workflow that supports any project, team or client interaction.
Purpose: Capture conversations from meetings, sales calls and field visits and convert them into structured information. Instead of pouring through raw recordings, the assistant automatically summarizes key points and extracts action items.
How it works: After a client visit, the professional calls the assistant. The assistant records the conversation, asks follow‑up questions to ensure all details are captured and then produces a structured summary. Key decisions, client preferences and next steps are extracted as tasks.
Best practices:
- Integrate with voice APIs such as Zoom, Teams or phone systems so that recordings are automatically passed to the assistant.
- Use large language models (LLMs) to produce readable summaries rather than dumping verbatim transcripts. Summaries are easier to consume and search.
- Configure the assistant to extract dates, addresses and other entities into discrete fields for downstream scheduling and CRM updates.
Purpose: Triage and respond to inbound emails, chat messages and text messages. The assistant prioritizes urgent requests, drafts responses and converts conversations into tasks.
How it works: The assistant monitors the user’s inbox and chat channels. It identifies emails that require immediate attention, generates suggested responses for routine questions and adds follow‑up reminders to the user’s task list. If a client requests a schedule change, for example, the assistant updates the calendar automatically and confirms with all parties.
Best practices:
- Define prioritization rules (e.g., VIP clients versus general inquiries) so the assistant knows when to alert the user.
- Train the assistant on the organization’s tone and frequently asked questions so that drafted responses are on brand.
- Feed metadata about email volume and response times into dashboards for analytics.
Purpose: Manage calendars, schedules and task lists. The assistant ensures that commitments are met, optimises meeting times and sends daily briefings.
How it works: The assistant synchronises with Google Calendar, Outlook or other scheduling systems. It automatically schedules follow‑up meetings, resolves conflicts, optimises travel routes for field visits and produces a morning briefing outlining the day’s tasks and appointments. When tasks arise from transcription or email, they are added to the schedule automatically.
Best practices:
- Allow the assistant to reschedule non‑critical meetings when new priorities emerge.
- Integrate location data for field teams so that travel times are considered when booking appointments.
- Send a daily digest via email or voice call summarizing key tasks, meetings and deadlines.
Purpose: Handle recurring operational tasks such as reporting, compliance checks and work order processing. The assistant automates routine steps and alerts managers when something requires attention.
How it works: At the end of each day, the assistant compiles notes from calls and visits, generates reports for management, updates inventory or order systems and checks that all tasks have been completed. If key performance indicators (KPIs) fall outside of acceptable ranges, the assistant escalates issues.
Best practices:
- Automate end‑of‑day, weekly and monthly reporting so that managers always have up‑to‑date metrics.
- Define exception thresholds. The assistant should only interrupt managers when an anomaly occurs or when approval is required.
- Integrate the assistant with compliance systems so that mandatory reporting (e.g., HIPAA, financial audits) happens automatically.
Purpose: Manage follow‑ups and nurture customer relationships through personalised outreach campaigns. The assistant sends timely messages and reminders based on CRM data and task lists.
How it works: When the CRM indicates that a follow‑up is due, the assistant drafts a personalised email or text message and sends it to the client. It monitors responses, schedules any requested meetings and logs all interactions back into the CRM. Outreach can be proactive (nurture campaigns) or reactive (confirmation messages after a meeting).
Best practices:
- Train the assistant on the company’s tone and product details to ensure messages are consistent.
- Use scoring to prioritise leads based on engagement history or purchase likelihood.
- Automate drip campaigns and reminders for contract renewals or service maintenance.
Purpose: Maintain accurate, structured client and project data. The assistant eliminates manual data entry and ensures that the CRM reflects the latest conversations and transactions.
How it works: After each transcribed call or email exchange, the assistant validates and updates contact details, notes and preferences in the CRM. It creates follow‑up tasks and logs outcomes. If an address is missing or inaccurate, it prompts the user for confirmation.
Best practices:
- Use the assistant to enrich data by cross‑checking with external sources (e.g., validating addresses or phone numbers).
- Build gap detection: the assistant should highlight missing fields or inconsistent data for manual review.
- Ensure two‑way synchronization: updates made manually in the CRM propagate back to the assistant’s task lists.
Purpose: Analyse patterns across the system and suggest improvements. The assistant continuously refines workflows based on performance data and user feedback.
How it works: The assistant aggregates data from transcription, inbox, scheduling, operations and outreach modules. It looks for trends—such as delays in follow‑ups or repetitive bottlenecks—and recommends adjustments. For example, if clients frequently ask the same question after demos, the assistant might suggest an automated follow‑up email that addresses those concerns.
Best practices:
- Generate weekly or monthly iteration reports that highlight successes and areas for improvement.
- Allow the assistant to propose small workflow changes (e.g., shifting meeting reminders from 24 to 48 hours) and measure their impact.
- Incorporate analytics tools (e.g., dashboards, performance metrics) to monitor how changes affect productivity and customer satisfaction.
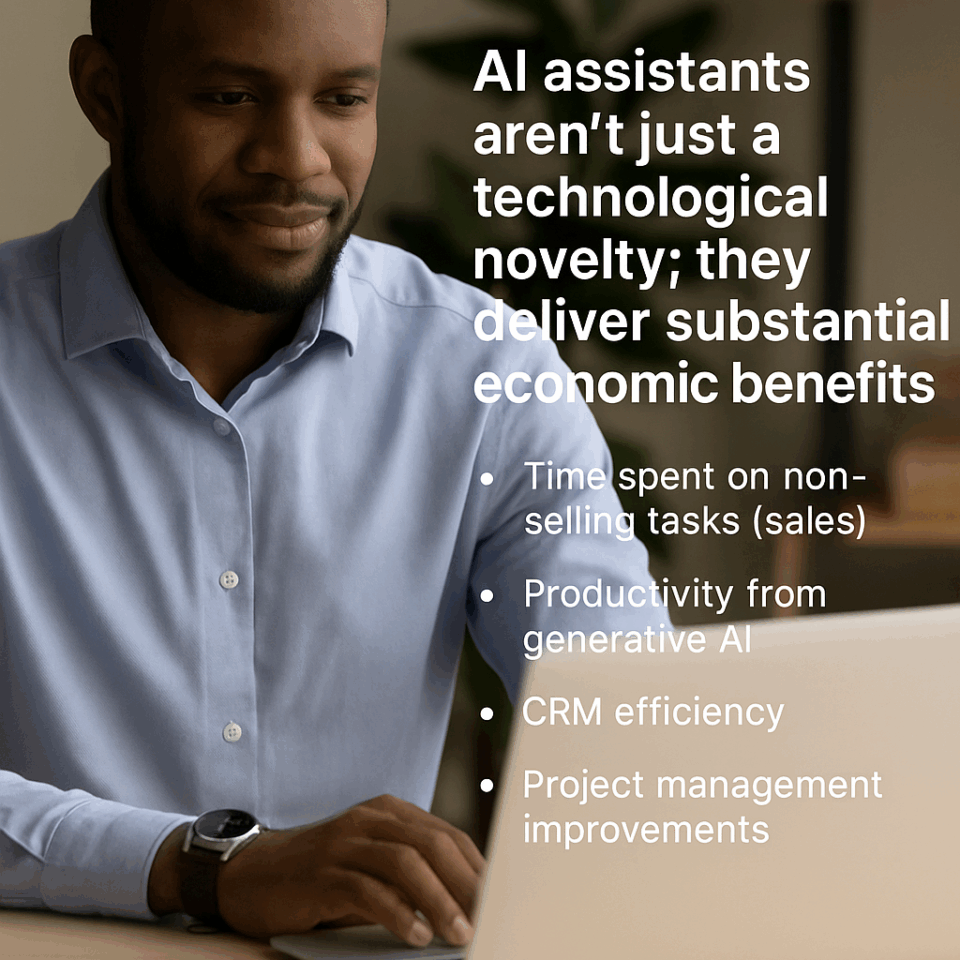
Return on Investment & Time‑Savings
AI assistants aren’t just a technological novelty; they deliver substantial economic benefits. Studies across sales, service and project teams show how automation and generative AI deliver dramatic productivity gains.
Metric | Baseline | AI‑Assisted Gain | 20× Impact Potential |
Time spent on non‑selling tasks (sales) | Sales representatives typically spend 65–70 % of their day on administrative work. | Automation can reclaim up to 5.5 hours per week, allowing reps to spend more time with clients. | By removing manual reporting and follow‑ups, throughput can be multiplied across the team. |
Productivity from generative AI | In early trials, generative AI boosts task throughput by 66 % to 126 % across knowledge work. | AI assistants handle routine writing, scheduling and research, freeing human workers for complex tasks. | Compound improvements across modules (transcription + scheduling + CRM) lead to 20× overall efficiency. |
CRM efficiency | CRM adoption delivers an average return of $8.71 for every $1 invested and can drive 41 % revenue growth. | AI integration reduces data entry time by 32 % and improves data quality. | Accurate, automated data feeds improve forecasting and customer satisfaction, amplifying revenue gains. |
Project management improvements | Traditional project teams waste significant time on status meetings and manual updates. | AI assistants cut reporting time by 40 % and increase sprint velocity by 15–40 %. | With real‑time insights and automated coordination, projects can complete sooner with higher quality. |
These metrics illustrate how small time savings add up across an organisation. When compounded across hundreds of interactions and tasks, enterprises can realistically achieve 20× improvements in quality, throughput and optimisation.
| Metric | Baseline | AI Assisted Gain | 20x Impact Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time spent on non‑selling tasks (sales) | Sales representatives typically spend 65–70 % of their day on administrative work./td> | Automation can reclaim up to 5.5 hours per week, allowing reps to spend more time with clients. | By removing manual reporting and follow‑ups, throughput can be multiplied across the team. |
| Productivity from generative AI | In early trials, generative AI boosts task throughput by 66 % to 126 % across knowledge work. | AI assistants handle routine writing, scheduling and research, freeing human workers for complex tasks. | Compound improvements across modules (transcription + scheduling + CRM) lead to 20× overall efficiency. |
| CRM efficiency | CRM adoption delivers an average return of $8.71 for every $1 invested and can drive 41 % revenue growth. | AI integration reduces data entry time by 32 % and improves data quality. | Accurate, automated data feeds improve forecasting and customer satisfaction, amplifying revenue gains. |
| Project management improvements | Traditional project teams waste significant time on status meetings and manual updates. | AI assistants cut reporting time by 40 % and increase sprint velocity by | With real‑time insights and automated coordination, projects |
ROI Highlights
01
CRM Integration
CRM integration yields an $8.71 return per $1 spent, drives 41 % revenue growth and reduces data entry time by 32 %.
02
Automation
65–70 % of sales time is spent on non-selling tasks. Automation can reclaim 5.5 hours per week per rep, multiplying capacity across teams.
03
Increase Efficiency
Project teams see reporting times cut by 40 % and sprint velocity increased by 15–40 %.
04
Eliminate Repetition
Generative AI improves task throughput by 66–126 %, eliminating repetitive writing, scheduling and research.
By compounding these improvements across transcription, scheduling, CRM and outreach, enterprises can achieve 20× gains in throughput, quality and project performance.
Industry Applications
- Use case: Software development teams often hold daily stand‑ups, sprint planning and code reviews. The assistant transcribes meetings, extracts action items and updates project tracking tools. It schedules code reviews and follow‑ups automatically. It also monitors support tickets and drafts responses.
- Benefits: Developers spend less time on status updates and more time coding. Project managers gain real‑time visibility into task completion and resource utilisation.
- Diagram:
Developer Meeting → Transcribe → Task Extraction → Schedule → Ops (sprint report) → Outreach (stakeholder update) → CRM (issue tracking) → Iterate
- Use case: Technicians record site visits using the assistant. It logs work performed, captures materials used and generates service reports. It updates inventory systems, schedules return visits and notifies customers of completion. Managers receive automatic job status updates.
- Benefits: Reporting times shrink; inventory levels stay accurate; customers receive consistent communication; repeat visits are scheduled promptly.
- Diagram:
Site Visit → Transcribe → Work Report → Schedule → Ops (inventory update) → Outreach (completion notice) → CRM (job record) → Iterate
- Use case: A logistics company manages hundreds of vehicles. After each delivery, drivers call the assistant to report issues and confirm completion. The assistant updates the dispatch schedule, logs maintenance tasks and notifies mechanics. It sends customers automated delivery confirmations and collects feedback.
- Benefits: Fewer breakdowns due to proactive maintenance; faster dispatch times; improved customer communication and satisfaction.
- Diagram:
Driver Call → Transcribe → Maintenance Task → Schedule → Ops (fleet report) → Outreach (delivery confirmation) → CRM (customer record) → Iterate
- Use case: A logistics company manages hundreds of vehicles. After each delivery, drivers call the assistant to report issues and confirm completion. The assistant updates the dispatch schedule, logs maintenance tasks and notifies mechanics. It sends customers automated delivery confirmations and collects feedback.
- Benefits: Fewer breakdowns due to proactive maintenance; faster dispatch times; improved customer communication and satisfaction.
- Diagram:
Driver Call → Transcribe → Maintenance Task → Schedule → Ops (fleet report) → Outreach (delivery confirmation) → CRM (customer record) → Iterate
- Use case: Store associates use the assistant to report daily sales floor observations. The assistant summarises customer feedback, inventory shortages and competitor promotions. It updates merchandising plans, schedules restocking and sends targeted offers to loyalty members.
- Benefits: Faster response to market trends; improved inventory accuracy; personalised customer outreach that increases conversion rates.
- Diagram:
Associate Report → Transcribe → Product Insights → Schedule → Ops (restock order) → Outreach (marketing offer) → CRM (loyalty program) → Iterate
- Use case: Financial advisors conduct client reviews using the assistant. It records goals, captures risk tolerance and updates portfolio management systems. It schedules follow‑ups, ensures compliance documentation is complete and sends summary reports to clients.
- Benefits: Advisors spend less time on paperwork; compliance audits are easier; client satisfaction increases due to timely communication.
- Diagram:
Client Review → Transcribe → Investment Action Items → Schedule → Ops (regulatory report) → Outreach (client summary) → CRM (portfolio record) → Iterate
Enterprise AI Project Assistants embody the next generation of productivity. By unifying transcription, email management, scheduling, operations automation, outreach, CRM and continuous improvement, they eliminate administrative friction and allow professionals to focus on what matters. The result is a 20× improvement in quality, quantity, throughput and overall project performance. Whether in software development, logistics, healthcare, construction, retail or finance, the principles remain the same: let the AI handle the busywork so that people can deliver exceptional value.

